Project Overview
The recent pandemic has raised alarms to focus on one of the most important aspects of development - Health Care Management. While health care data has various uses we are focusing on observing and predicting one of the critical parameters - patients length of stay. This parameter helps hospitals to identify patients who will stay longer at the time of admission . This helps in logistics such as resource allocation. The task is to accurately predict the length of stay for each patient case by case so that hospitals can use this information for optimal resource allocation and better functioning. The data contains 18 parameters, some of the relates of the patient such as age, severity of illness, department, type of admission and some other information related to location such as city, hospital region and hospital type etc. The project goal is to build an end to end application that ingests tabular data and uses Google auto ML platform to train a model and then run predictive analysis on new data incoming data. We are trying to replicate a production level architecture using kubernetes, messaging queue, cloud function, data storages and autoML tools.Project Goals
In this project, we are trying to develop an application whose architecture replicates a real-world application with high transactions per second (Tps) and how to distribute the load uniformly across components. We are using the Google Kubernetes cluster, which is reliable and fault-tolerant towards node failures and has the auto-restart capability. Using a messaging queue to process the load without waiting for acknowledgment and also the separation of concern. Google cloud function is a lightweight pod that is activated on an event and shut down on completion of its task. Finally using AutoML, we are first trying to use cloud capability to perform heavy ML tasks like training models and later making predictions on the top of it. The cloud technologies used are -
Architectural Diagram
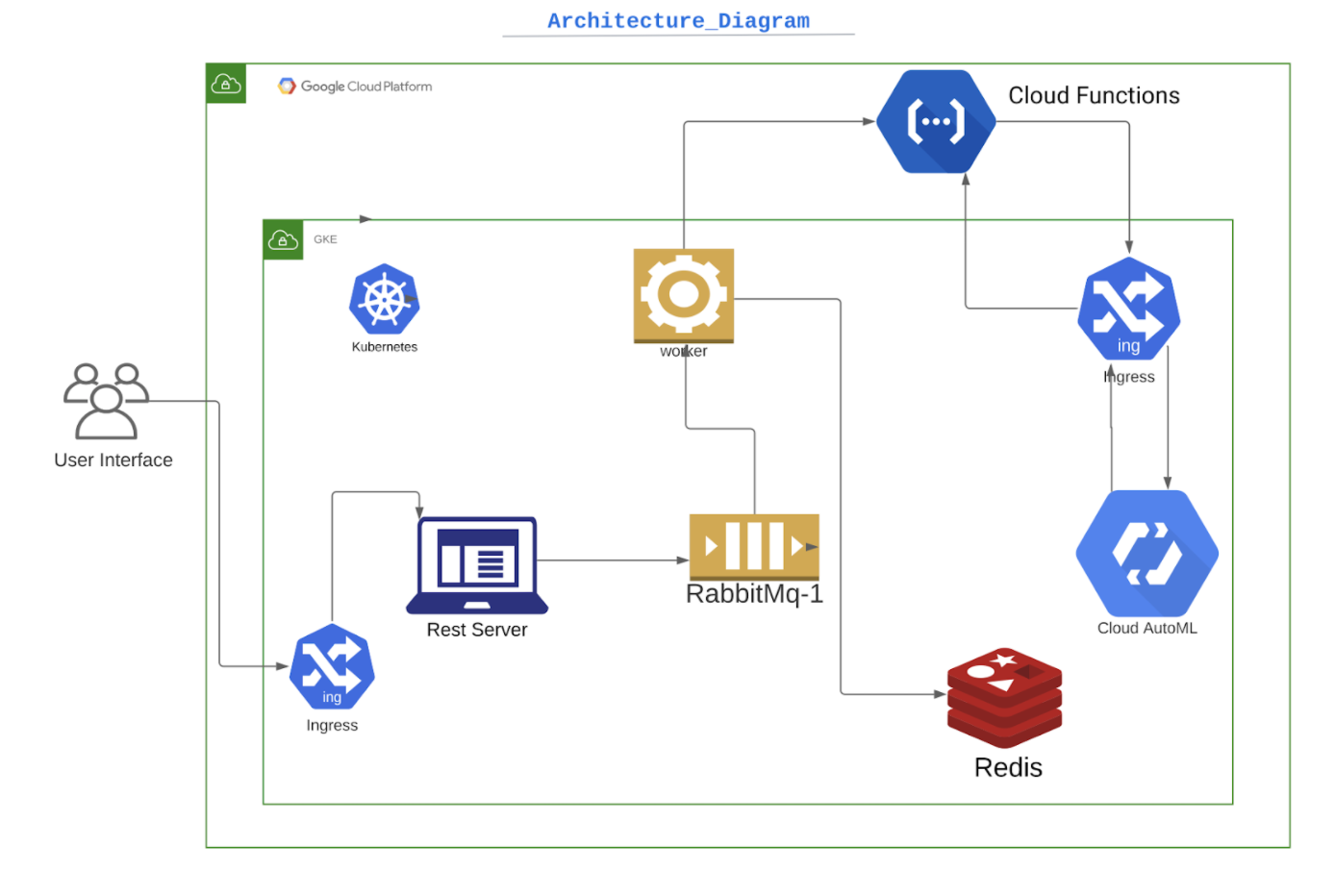
Software Components used
REST API
We used the Python Flask library to write Rest Apis. It is a user friendly and easy to use framework. We wrote apis to expose our services to be used by other applications or user interfaces. Key api exposed for this application were: POST : /medical/insert Inserts a new record in persistent storage via rabbitMq and triggers a google cloud function in parallel to get the forecast data for the record. GET: /medical/forecast/lengthofstay Gets the forecast of field Length_of_stay for a new patient record, from redis if its forecast data is successfully fetched from the trained model server. GET: /medical/forecast/dump Gets a dump of forecasted data stored in redis for each patient_id for debugging purposes. GET: /medical/fetch Take patientId as a request parameter and fetches all the case details for that particular patient, if exists else it returns an error message. GET: /medical/dump Dumps all the data from redis, after aggregating the data for each patient. This data can be consumed by the dashboard to display patient details.
Rabbit MQ
After the patient data is received from the user by rest api, the rest api pushes the data to rabbit mq which is then consumed by the worker to do further processing. We used RabbitMQ because it is an easy way to send messages between two processes and it ensures reliable delivery i.e it waits for an acknowledgement. So if the worker process is down it will try to send the data again. The disadvantage is that we can send only small chunks of data using rabbitmq.
Redis
Redis is used as a storage, the worker process uses this to store the patient Data after it has received the prediction from the cloud function. The rest API queries the redis DB to get patient information or the predicted values. The data is stored in the form of patientID:caseID since you can have multiple cases for the same patient. We used redis because it is a fast in memory database with simple key value pairs. The disadvantage would be the record size was huge then redis would perform badly also the data is not persistent in case of restart.
Worker
Worker is the processing unit, it receives the patient data from the rest API via rabbitmq and calls the cloud function to get the predicted length of stay for the patient and store it in the redis database.
Google Auto ML
We took the training data set from kaggle and provided that as an input to Auto ML which did the classification. The training set has 10 different classes 0-10, 10-20 and so on till more than 100 days. The tensor flow model was then exported and pushed as an image in google container registry to use as docker container. The advantage of using this is that we don’t need to use ML libraries manually and perform tests and trials. The software does a good job at configuring the parameter scores to return an fairly accurate model. The disadvantage is that it is compute heavy tasks and has higher resource requirements.
Cloud functions
We used cloud functions for sending request to docker container running the tensor flow model. The worker sends the patient data to the cloud function which then sends it to the tensor flow model and returns the scores of each label to the worker. The advantage of using cloud functions is that this can be an independent service that can be used by multiple projects.
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
We used GKE to deploy our applications. We used an ingress to expose the REST API and prediction service. All the applications such as REST API, worker were pushed as docker images and then used as services with GKE. The prediction model was pulled from the google container registry. The advantage of using GKE is that we can easily deploy the application and see the logs. Also if any service goes down the GKE will try to respawn it. It's easier to increase the number of replicas in case of increased load.
Training & Testing
We took the training and testing dataset from kaggle https://www.kaggle.com/nehaprabhavalkar/av-healthcare-analytics-ii. We sampled our data set into two different samples: Train and Test. We used a train data set to train our model using google cloud AutoML, which uses tensor flow to run regression as a service and generate a model on the tabular data provided as training data set.
The solutions that we designed can be scaled for larger use cases very easily, as we have used google kubernetes cluster for deploying our services. However if and when the medical data set changes with newer parameters we will need to re-train the tensor flow model which can easily create a significant overhead as it is a compute heavy task. Although we are currently unaware of any existing solution for this issue, further research can help us come up with efficient solutions to overcome this bottleneck.
